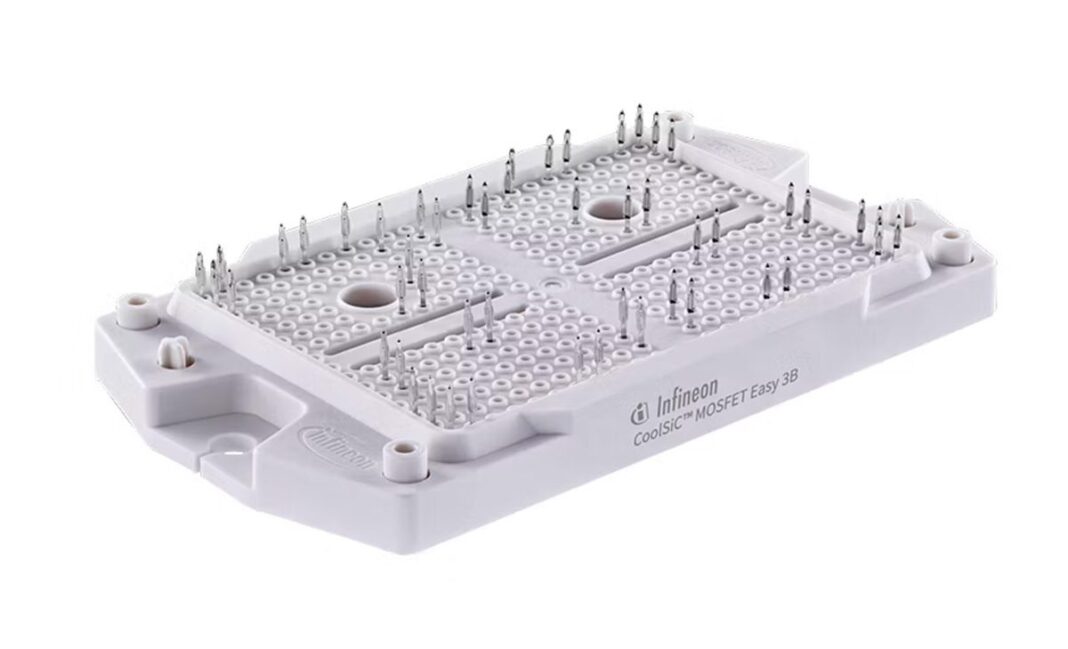
Infineon Technologies has announced that it will supply custom silicon carbide (SiC) power modules to Electreon for use in Electreon’s dynamic in-road wireless charging system for EVs. This electric road system enables buses, trucks and other EVs to charge wirelessly while in motion using inductive charging via copper coils embedded beneath roadway surfaces.
The system interfaces directly with the power grid and activates when vehicles are positioned above the coils, providing real-time energy transfer and continuous battery charging. Infineon reports that its EasyPACK 3B CoolSiC 2,000 V SiC modules, specially developed for Electreon’s requirements, form the core of the system’s power electronics.
These modules facilitate energy conversion from the power grid for wireless battery charging, with an average power transfer of 200 kW and peaks exceeding 300 kW. This performance was recently confirmed during operation on France’s A10 highway, which Electreon claims is the first highway able to wirelessly charge moving heavy- and medium-duty trucks, buses, vans, and passenger cars.
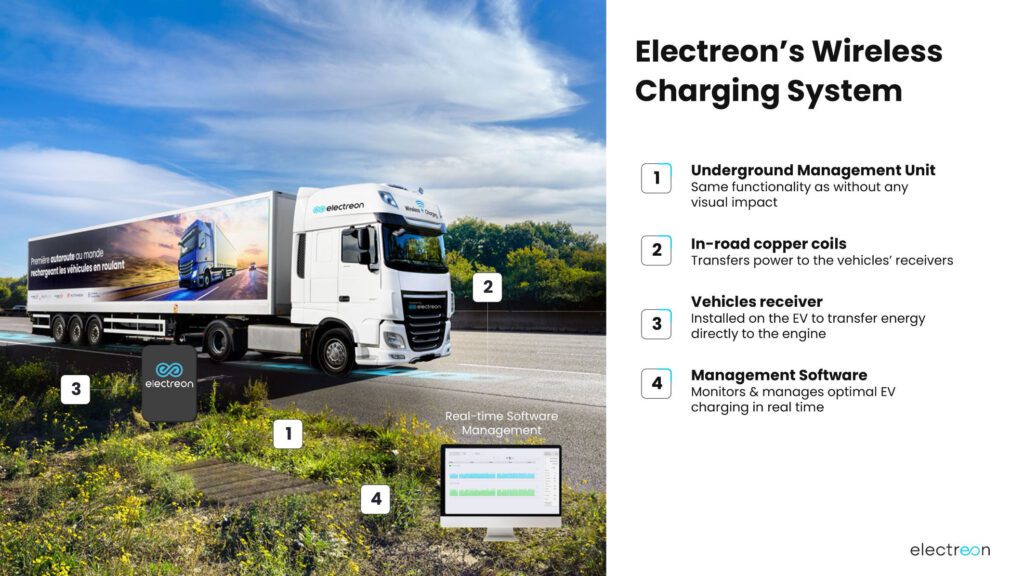
The in-road wireless charging system allows vehicles to operate with smaller batteries by recharging on the move, potentially lowering upfront costs and vehicle weights while increasing cargo capacity. Electreon has deployed Infineon’s SiC modules across test tracks in the US, Germany, France, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Italy, Israel, and Japan, and plans to integrate the technology into additional long-distance projects.
“Electreon’s wireless charging system is a real game changer on the road to reducing carbon emissions in transportation,” said Dominik Bilo, Executive Vice President and Chief Sales Officer Industrial & Infrastructure at Infineon Technologies. “We’re proud to contribute to this groundbreaking innovation with our customized SiC power modules, which efficiently convert electrical energy to charge vehicles on the go, tailored to meet Electreon’s specific needs.”
Silicon carbide-based semiconductors are noted for handling high power at higher switching frequencies and lower losses than traditional silicon, allowing for compact and robust designs ideal for EV charging applications.
Source: Infineon Technologies