Sponsored by TTI.
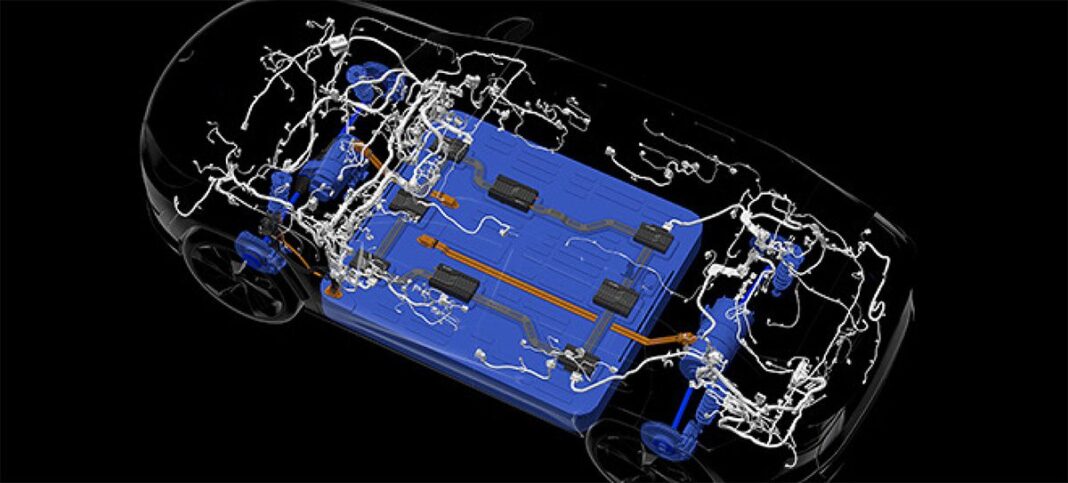
Even without taking the transition from internal combustion engines to battery electric vehicles into account, the electrical power requirements of today’s vehicles have become daunting. Every device within a vehicle—from the air conditioner and seat heaters to the lighting and infotainment systems — requires power, and the wires supplying that power must have a large enough diameter to support the current.
One way to reduce the wire gauges, weight and cost throughout is to transition from a 12 V electrical architecture to one based on 48 V. But OEMs that move to 48 V have to pay particular attention to several key design considerations to ensure the system’s safety and reliability.